

Next: Binary Triflexagon Cutouts
Up: First Level Triflexagon
Previous: Tukey triangle
Figure 8:
Permutation of the triangles along the strip for a normal triflexagon. They run in order, subject to being flipped over, so the permutation is the identity.
 |
Figure 9:
Top side of the
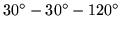 triangle cutout. Together with its backside, the figure displays one single flexagon with six sectors, the minimumum requirement to lie flat on account of the
triangle cutout. Together with its backside, the figure displays one single flexagon with six sectors, the minimumum requirement to lie flat on account of the 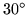 angle.
angle.
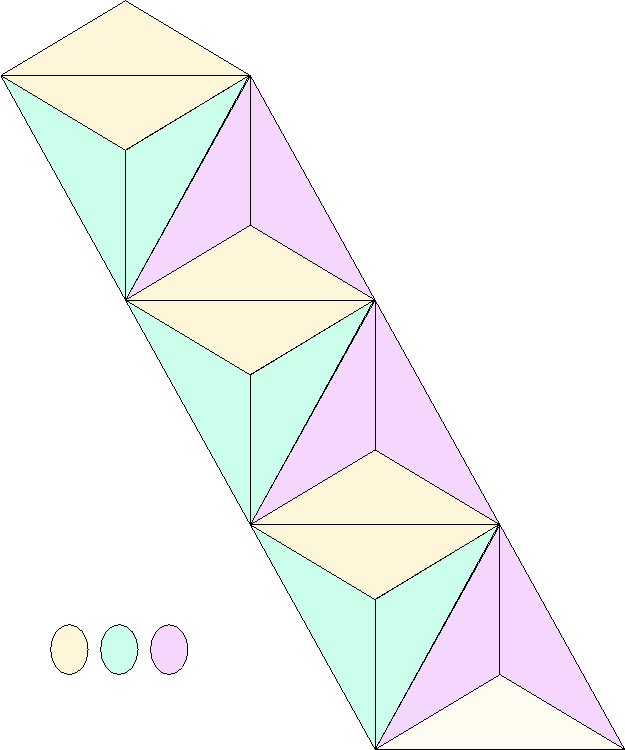 |
Figure 10:
Bottom side of the
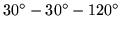 triangle cutout.
triangle cutout.
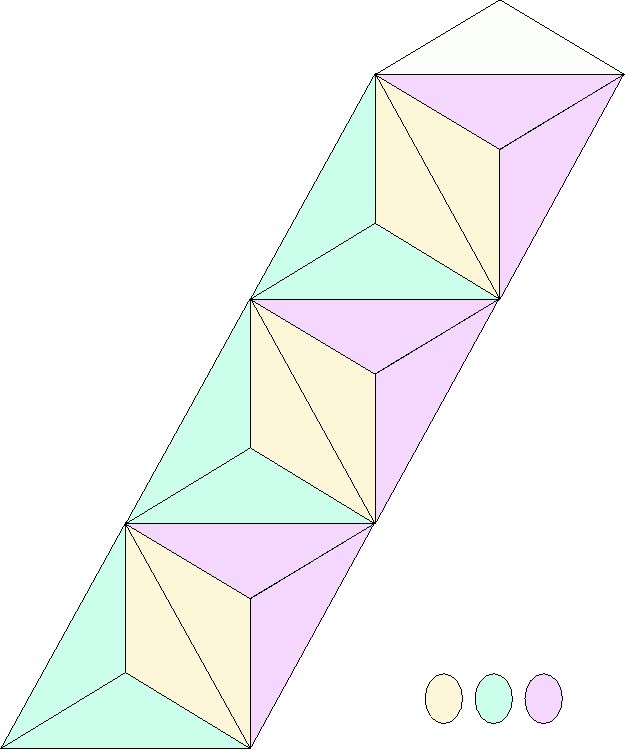 |
Figure 11:
Top side of the
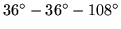 triangle cutout. Together with its backside, the figure displays one single flexagon with five sectors, the minimumum requirement to lie flat on account of the
triangle cutout. Together with its backside, the figure displays one single flexagon with five sectors, the minimumum requirement to lie flat on account of the 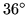 angle.
angle.
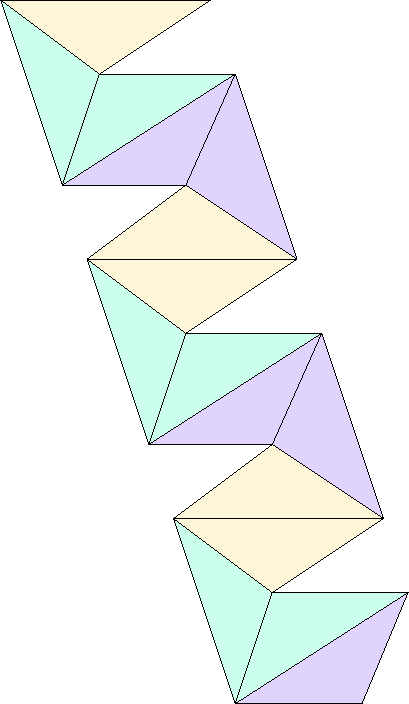 |
Figure 12:
Bottom side of the
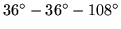 triangle cutout.
triangle cutout.
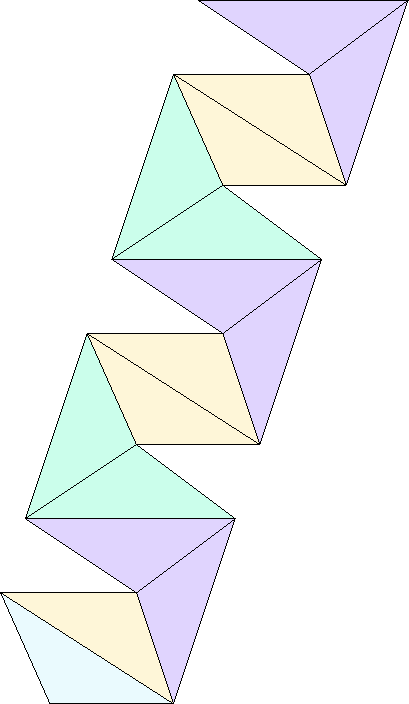 |
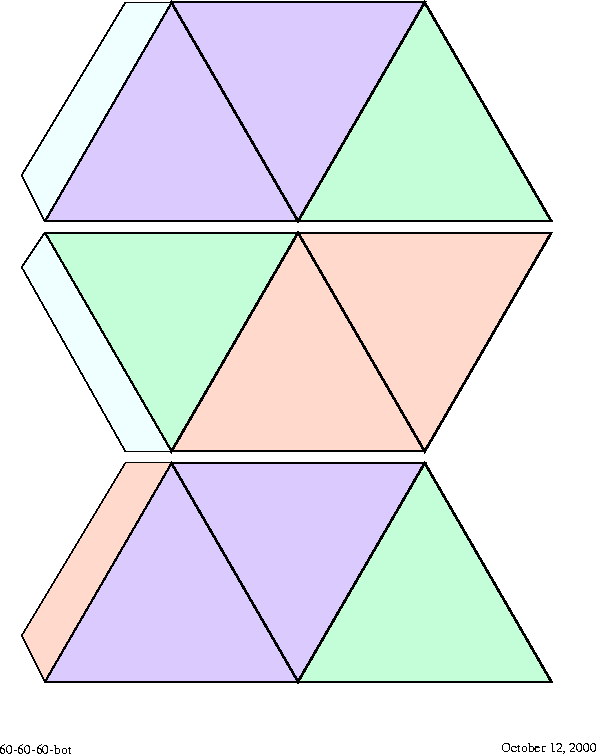
Figure 13:
Top side of the
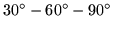 triangle cutout. Together with its backside, the figure displays one single flexagon with six sectors, the minimumum requirement to lie flat on account of the
triangle cutout. Together with its backside, the figure displays one single flexagon with six sectors, the minimumum requirement to lie flat on account of the 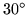 angle.
angle.
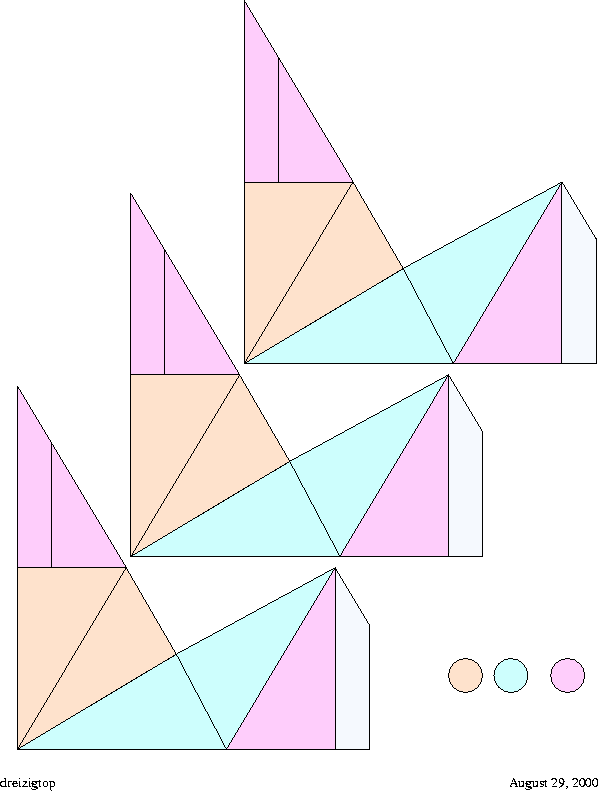 |
Figure 14:
Bottom side of the
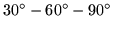 triangle cutout.
triangle cutout.
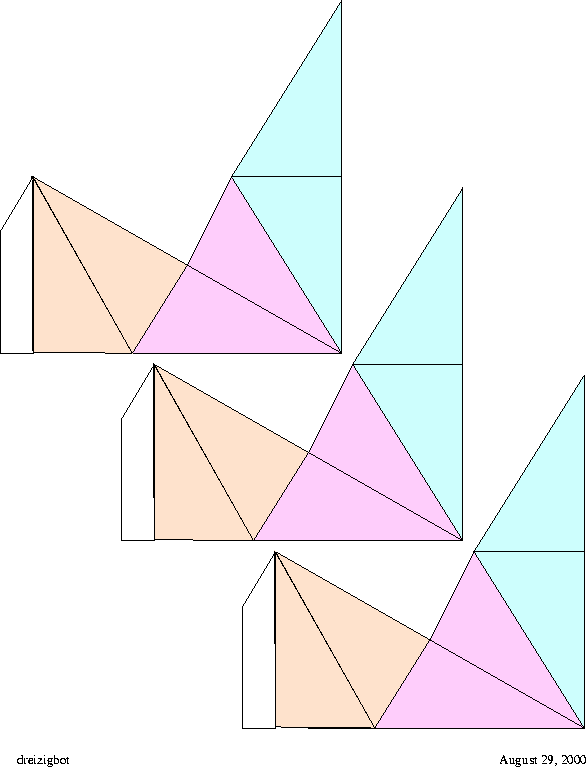 |
Figure 15:
Top side of the
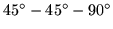 triangle cutout. Together with its backside, the figure displays one single flexagon with four sectors, the minimumum requirement to lie flat on account of the
triangle cutout. Together with its backside, the figure displays one single flexagon with four sectors, the minimumum requirement to lie flat on account of the 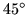 angle.
angle.
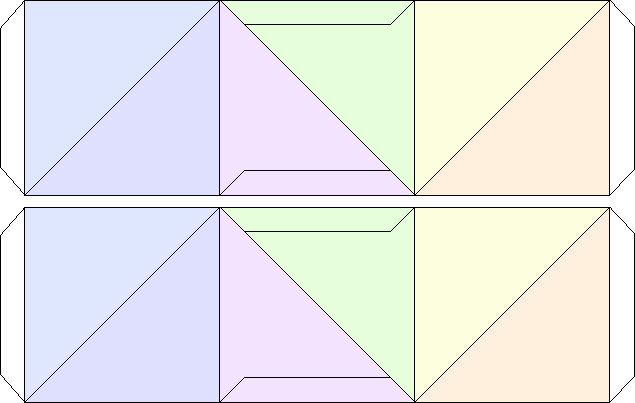 |
Figure 16:
Bottom side of the
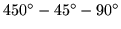 triangle cutout.
triangle cutout.
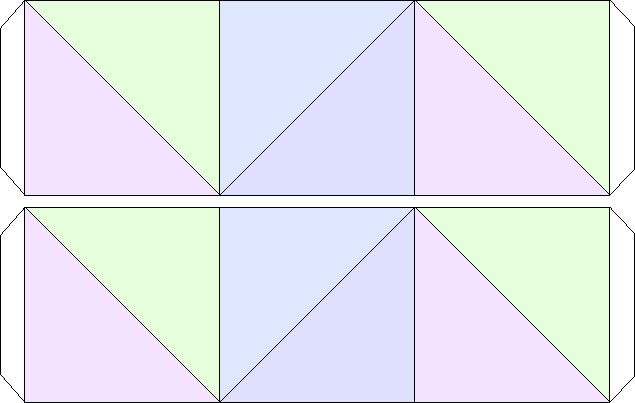 |
Figure 17:
Top side of the first level normal triflexagon cutout. Together with its backside, the figure contains one single triflexagon.
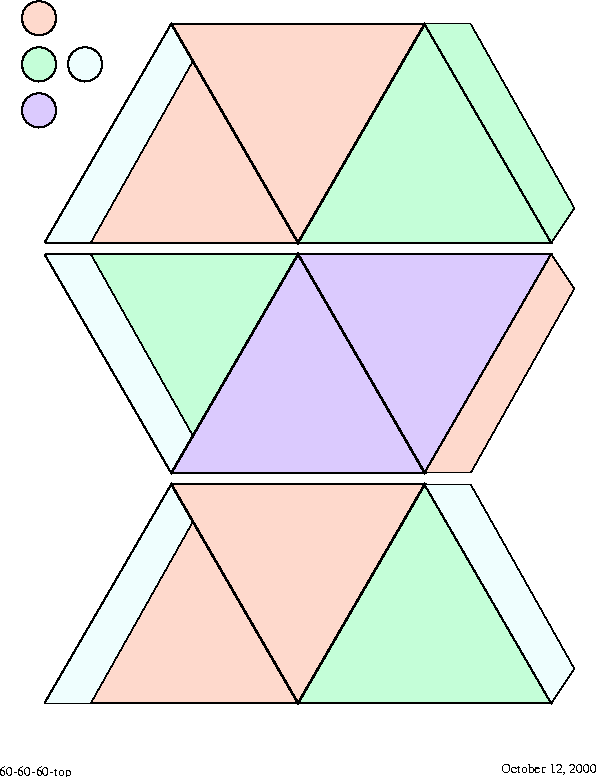 |
Figure 18:
Bottom side of the first level normal triflexagon cutout. Together with its backside, the figure contains three triflexagons.
 |



Next: Binary Triflexagon Cutouts
Up: First Level Triflexagon
Previous: Tukey triangle
Microcomputadoras
2000-11-01