


Posterior: About this document ...
Anterior: Problemas típicos de lógicas
- 1
- Barwise (ed): Handbook of Mathematical Logic, Studies in Logic and the Foundations of Mathematics, Vol. 90. North-Holland Publishing Co., 1977.
- 2
- Bauer, P., Nouak, S., Winkler, R. A brief course in
fuzzy logic and fuzzy control, disponible en
ftp.flll.uni-linz.ac.at/pub/info/, 1996.
- 3
- Blanche: Axiomatics, The Free Press of Glencoe, New York, 1962.
- 4
- Bell, Machover: Introduction to Mathematical Logic, North-Holland, 1978.
- 5
- Bell, Slomson: Models and Ultraproducts: An Introduction, North-Holland, 1969.
- 6
- Bolc, Borowik: Many-valued Logics, Springer-Verlag, 1992.
- 7
- Boolos, George S. The Logic of Provability. Cambridge University Press.
- 8
- Boolos, George S., and Jeffrey, Richard C.: Computability and Logic. Cambridge University Press, 2nd edition, 1980.
- 9
- Boyer, Moore: A Computational Logic. Academic Press, 1979.
- 10
- Chellas: Modal Logic: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press, 1980.
- 11
- Church: An Introduction to Mathematical Logic. Part 1. Princeton University Press, 1967.
- 12
- Clocksin, Mellish: Programming in Prolog, Springer-Verlag, 1981.
- 13
- Cuena: Lógica Informática, Alianza Informática, 1987.
- 14
- Chang, Lee: Symbolic Logic and Mechanical Theorem Proving.
Academic Press, 1973.
- 15
- Davis: The Undecidable. Basic Papers on Undecidable Propositions, Unsolvable Problems and
Computable Functions. Raven Press, 1965.
- 16
- Dempster, A. P. A generalization of Bayesian inference,
J. Roy. Stat. Soc., B30, pp. 205-247, 1968.
- 17
- Dubois, D., Prade, H. Fuzzy sets in approximate reasoning II
(Logical approaches), Fuzzy sets and systems., 40, pp.
203-244, 1991.
- 18
- Dubois, D., Prade, H. Fuzzy sets and systems: Theory
and applications, Academic Press, 1980.
- 19
- Enderton, A Mathematical Introduction to Logic, Academic Press, 1972.
- 20
- Fagin, Halpern, Yoram, Vardi: Reasoning about Knowledge. MIT Press, Cambridge, 1995.
- 21
- Fisher, Groarke, Tindal: Good Reasoning Matters: A Constructive Approach to Critical Thinking (second edition). Oxford University Press, 1997.
- 22
- M. Fitting: FirstÂ-Order Logic and Automated Theorem Proving. Springer, 2nd edition, 1996.
- 23
- Gabbay, Hogger, Robinson, (editors): Handbook of Logic in Artificial Intelligence and Logic Programming, Oxford University Press, 1993.
- 24
- Gallier: Logic for Computer Science. John Wiley, 1987.
- 25
- Genesereth, Nilson: Logical foundations of Artificial
intelligence. Morgan Kauffman, 1987.
- 26
- Gödel, Kurt. 1931. On formally undecidable propositions of Principia mathematica and related systems I. In Gödel, 1986, pp. 145-195. Originally published as ``Über formal unentscheidbare Sätze der Principia mathematica und verwandter Systeme I'', Monatshefte für33 Mathematik und Physik, 38, pp. 173-198.
- 27
- Gödel, Kurt. 1986. Collected Works, vol. I. Oxford University Press.
- 28
- Grassmann, Tremblay: Logic and Discrete Mathematics: A Computer Science
Perspective. Prentice-Hall, 1996.
- 29
- Halperu: Theoretical Aspects of Reasonning about Knowledge.
Morgan Kauffman, 1986.
- 30
- Hamilton: Logic for Mathematicians. Cambridge University Press, 1978.
- 31
- Hájek, P., Godó Ll. Deductive systems of fuzzy
logic, unpublished manuscript, 1997.
- 32
- Hilbert, David. 1927. The foundations of mathematics. In van Heijenoort 1967, pp. 464-479. Originally published as ``Die Grundlagen der Mathematik'', Abhandlungen aus dem mathematischen Seminar der Hamburgischen Universität, 6, pp. 65-85.
- 33
- Hintikka, J. Knowledge and belief, Cornell University
Press, 1962.
- 34
- Hughes, Cresswell: Introducción a la Lógica Modal, Tecnos, 1973.
- 35
- Huth, Ryan: Logic in Computer Science: Modelling and Reasoning about Systems, Cambridge University Press, 1999.
- 36
- Jech, T., Set Theory, Academic Press, 1978.
- 37
- Kantrowitz, M. et al, FAQ: Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy
Expert Systems, disponible en
ftp.cs.cmu.edu:/user/ai/pubs/faqs/fuzzy/fuzzy.faq, (desde 1995).
- 38
- Kaufmann, A., Introducción a la teoría de los
subconjuntos borrosos, Cía. Editorial Continental, 1982.
- 39
- Kleene: Introduction to Metamathematics. Wolters-Noordhoff, 1980.
- 40
- Kleene: Mathematical Logic. Wiley, 1976.
- 41
- Kowalski R.: Logic for Problem Solving, North Holland, 1979.
- 42
- Lewis, Langford: Symbolic Logic. Dover, 1959.
- 43
- Liedl, H., Niederreiter, Introduction to Finite Fields and their Applications, Cambridge University Press, 1986.
- 44
- Lu: Mathematical Logic for Computer Science. World Scientific, 1989.
- 45
-
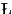 ukasiewicz, J. Selected works, North Holland, 1970.
ukasiewicz, J. Selected works, North Holland, 1970.
- 46
- Mac Lane, Birkhoff: Algebra. The Macmillan Co., 1967.
- 47
- Malitz: Introduction to Mathematical Logic: Set Theory, Computable Functions, Model Theory. Springer-Verlag, 1987.
- 48
- Manin: A Course in Mathematical Logic. Springer-Verlag, 1977.
- 49
- Manna, Pnueli: The Temporal Logic of Reactive and Concurrent Systems: Specification. SpringerVerlag, 1991.
- 50
- Mendelson: Introduction to Mathematical Logic. Van Nostrand
(Third Edition), 1987.
- 51
- Nagel, Newman: Godel's Proof. New York University Press, 1958.
- 52
- Nerode, Shore: Logic for Applications. Springer-Verlag, 1997.
- 53
- Nilsson: Principles of Artificial Intelligence. Morgan Kauffman, 1980.
- 54
- Paris, J., The uncertain reasoner's companion - a
mathematical perspective, Cambridge University Press, 1994.
- 55
- Pawlak, Z. Rough sets: Theoretical aspects of reasoning
about data, Kluwer Academic, 1991.
- 56
- Pelyani, Kowalski: Logic and semantic networks,
Communications of the ACM 22(3), 1979.
- 57
- Prawitz: Natural Deduction: A ProofÂ-Theoretical Study. Almqvist & Wiksell, 1965.
- 58
- Robinson: Logic: Form and functions: The Mechanization of Deductive Reasoning. North-Holland, 1979.
- 59
- Rogers: Mathematical Logic and Formalized Theories. A Survey of Basic Concepts and Results. North-Holland, 1974.
- 60
- Rosenbloom: The Elements of Mathematical Logic. Dover, 1950.
- 61
- Rubin: Mathematical Logic: Applications and Theory. Saunders College Publishing, 1990.
- 62
- Schöning: Logic for Computer Scientists. Birkhäuser, 1989.
- 63
- Schroeder, M., Schroeder, M. R., Number Theory In Science And Communication: With Applications In Cryptography, Physics, Digital Information, Computing, And Self-Similarity, Springer-Verlag Telos, 1997.
- 64
- Schweizer, B., Sklar, A. Probabilistic metric spaces,
North Holland, 1982.
- 65
- Shafer, G. A mathematical theory of evidence, Princeton
University Press, 1976.
- 66
- Shoenfield: Mathematical Logic, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., 1967.
- 67
- Smorynski: What's New in Logic?, Math. Intelligencer, 7, no. 3, 53-54, 1985.
- 68
- Sperschneider, Antoniou: Logic, A Foundation for Computer Science. Addison Wesley, 1991.
- 69
- Sterling, Shapiro: The Art of Prolog: Advanced Programming
Techniques. MIT Press, 1986.
- 70
- Van Benthem: The Logic of Time, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1983.
- 71
- van Dalen. Logic and Structure. Universitext. SpringerVerlag, 3rd edition, 1989.
- 72
- van Heijenoort, Jean (ed.). 1967. From Frege to Gödel: A Source Book in Mathematical Logic, 1879-1931. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
- 73
- Webb: Mechanism, Mentalism, and Metamathematics: An Essay on Finitism. Reidel, 1980.
- 74
- Wierzchon, S. Metody representacji i przetwarzania
informacji niepewnej w ramach teorii Dempstera-Shafera (en polaco),
Instytut Podstaw Informatyki, Polskiej Akademii Nauk, 1996.
- 75
- Zadeh, L. Fuzzy sets, Info. & Ctl., 8, 1965.
- 76
- Zadeh, L. Fuzzy logic, IEEE Computer, 1:83, 1988.
Guillermo Morales-Luna
2004-07-28