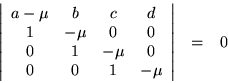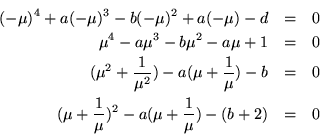


Next: Dynamical matrix symmetry
Up: Wave symmetry
Previous: wave matrices
Contents
A similar result applies to the 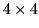 wave matrix of uniform second neighbor interactions,
wave matrix of uniform second neighbor interactions,
The sequence of indices is reversed by the self-inverse
so
while
This time it is 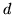 which should be
which should be 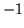 , although
, although 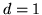 is also a possibility. Then it is also required that
is also a possibility. Then it is also required that 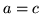 , so the recursion relation
, so the recursion relation
has to be symmetric with respect to reversing the order of the indices.
The characteristic equation of a 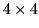 wave matrix reads
wave matrix reads
Laplace expansion by the first row gives
Thus 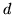 is the determinant, the product of all the roots, and should be
is the determinant, the product of all the roots, and should be 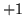 . Putting the other symmetry condition,
. Putting the other symmetry condition, 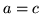 ,
,
As before, the roots occur in reciprocal pairs, as they should when a matrix is equivalent to its inverse.



Next: Dynamical matrix symmetry
Up: Wave symmetry
Previous: wave matrices
Contents
Pedro Hernandez
2004-02-28
![]() wave matrix of uniform second neighbor interactions,
wave matrix of uniform second neighbor interactions,
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\left[ \begin{array}{l} x_{i+2}\\ x_{i+1}\\ x_i\\ x_{i-1}\end...
...array}{l}x_{i+1}\\ x_i\\ x_{i-1}\\ x_{i-2} \end{array} \right].
\end{eqnarray*}](img535.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}
R & = & \left[ \begin{array}{cccc}
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0
\end{array} \right],
\end{eqnarray*}](img536.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\left[ \begin{array}{cccc}
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \...
... 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ d & c & b & a
\end{array} \right],
\end{eqnarray*}](img537.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\left[ \begin{array}{cccc}
a & b & c & d \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \...
...& 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & -a & -b & -c
\end{array} \right].
\end{eqnarray*}](img538.gif)
![]() wave matrix reads
wave matrix reads