


Next: Cook's G-gliders, backward velocity
Up: The Gliders
Previous: tiling approach to -8/30
Cook remarks that the F glider can be triggered from an A-C collision, the details of which are shown in Section 3.3.1.
Figure 2.30:
The lackadasical F glider, which moves 4 left in 36 generations, for a velocity of -1/9 c. Left: the unit cell, expressed with T tiles. Right: presentation with S tiles, showing the different approach aspects.
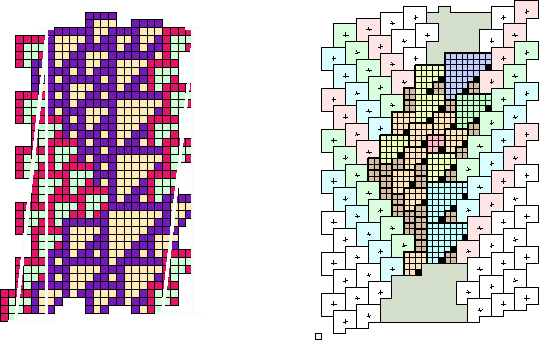 |
One period of an F glider occupies six ether files on the left, such as would be used in the approach of an A glider. However, it occupies only four files on the right, the path along which a B would approach. The difference is due, of course, to the differences in velocity between A's and B's.
Example user SuSE Linux 6.2
2000-05-19

